Do you want to know how IP addresses are assigned to devices connected to the Internet? Then read this article to learn how it is done.

The Internet protocol defines a set of principles on how data is transferred over the Internet, and IP addresses are an integral part of this. No computer is connected to the Internet without having an IP address assigned to it as it serves as a means of network interface identification without which communication is not possible.
IP addresses are assigned by Internet Service Providers (ISPs). One thing you need to know is that IP addresses are unique to every computer connected to the Internet and, as such, make each device unique. Some Internet users do not even know what an IP address is and what it is meant for. If you are one of those Internet users, then I will advise you to read our IP address 101 article first before proceeding.
In this article, we will be discussing how IP addresses are assigned. You will discover at the end of the article that even though your ISP is the one that assigns you an IP address, your IP address did not originate from the ISP – it has a route it followed before it got to the hand of your ISP.
Another thing you will learn is the difference between static IP addresses and dynamically assigned IP addresses. The article will be concluded with recommendations on how to use a different IP address other than the IP address assigned to you by your ISP to access the Internet.
IP Address Allocation Procedure

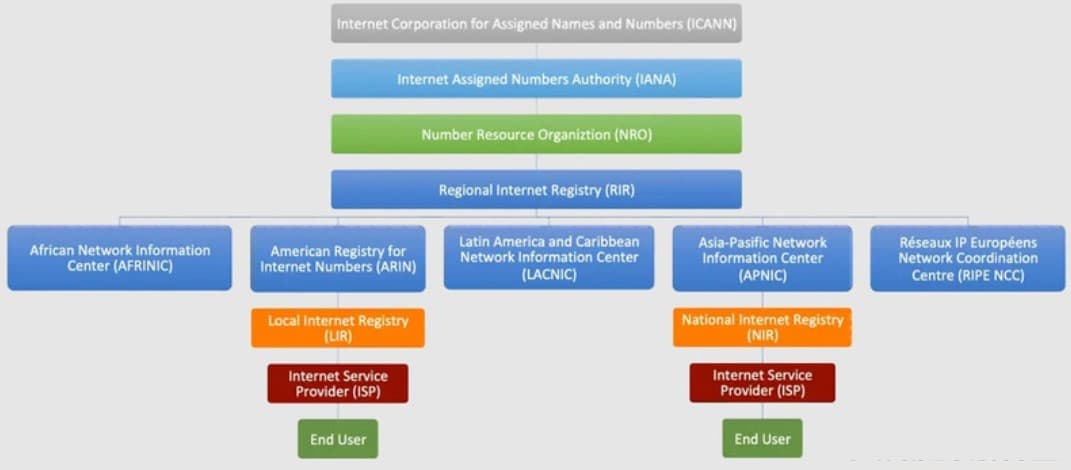
IP addresses are allocated to bodies that then allocate them to other smaller organizations under it before it gets to the final consumer or user, which is you and other users of the Internet. The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Number (ICANN) is the highest authority in this regard.
The ICANN is saddled with the responsibility of allocating IP address space, protocol identifier assignment, domain name management, and root server system management. For IP address allocation, it has a body known as the Internet Assigned Number Authority (IANA). The IANA is responsible for assigning IP addresses to local registrars.
Currently, there are about 5 local registrars, with each serving different locations. The AFRINIC serves Africa, ARIN serves the United States, Antarctica, Canada, and parts of the Caribbean. LACNIC servers most part of the Caribbean and all parts of Latin America. APNIC serves South Asia, Southeast Asia, East Asia, and Oceania. Lastly, RIPE NCC serves Europe, West Asia, and Central Asia, and Russia.
These local registrars assign the IP addresses assigned to them by IANA to ISPs which is responsible for allocating the IP address to end users’ devices. When IP addresses are assigned to ISPs, they are assigned in the form of blocks knowns as IP subnets. The number of IP addresses in a subnet varies depending on its type.
The Autonomous System Number (ASN) is a number assigned to an ISP that you can use to link any IP address with its ISP. ASN is unique to an ISP, and in most cases, an ISP is supposed to have only one ASN.
However, there are some large ISPs that have companies under them and, by so doing, having more than one ASN.So, in essence, the route an IP address pass before it gets to you is from ICANN to IANA, to the local registrar, which distributes them to ISPs responsible for assigning them to end-users.
- IPv4 Subnetting tutorial: How to Calculate Subnetting in IPv4
- IPv6 Subnetting tutorial: How to Calculate Subnetting in IPv6
How ISPs Assign IP Addresses
When ISPs receive IP addresses from their local registrar, they keep them in a pool of IP addresses from which they choose IPs to assign to their customers. Basically, there are two types of IP addresses in terms of IP assignment. Some IP addresses are static and do not change – these IPs are known as static IP addresses.
For these IPs, when they are assigned to you, you can keep them for as long as you want. Aside from static IPs, there are other types of IP addresses known as dynamic IP addresses. Most mobile IP addresses are dynamically assigned by their ISP – the process is the same as the method your router use in your home network.
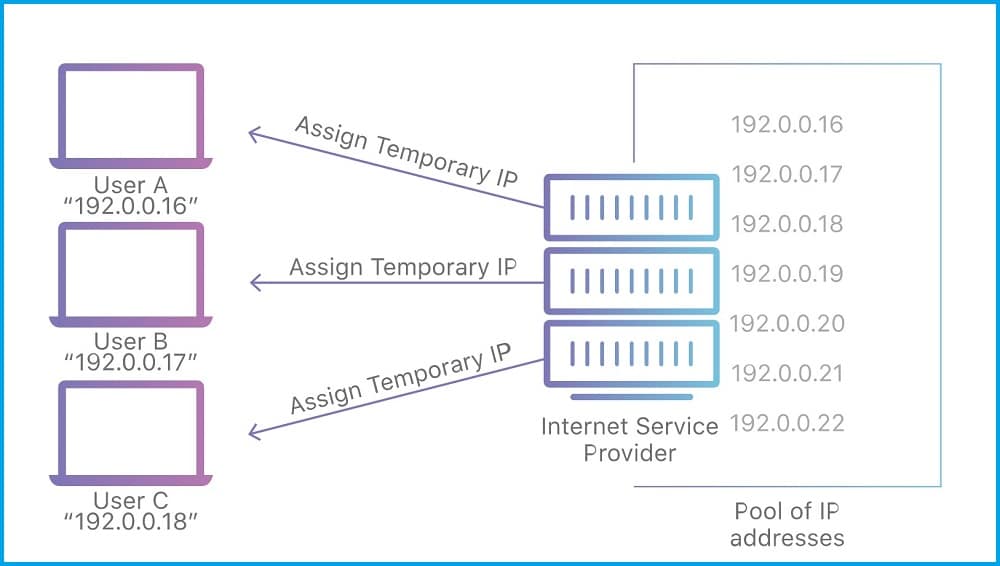
ISPs run DHCP servers that assign IP addresses to their customers dynamically. When you try to connect to the Internet, your ISP looks into their IP pool for an available IP address and assigns one to you.
When you disconnect your Internet access, the IP address is pulled back into the pool of available IPs to be reassigned to another customer. If you try accessing the Internet after a while, you will get another IP address other than the previous one. This happens because ISPs do not as many IP addresses to meet the demand.
How to Hide Your Real IP Address Online

When your ISP assigns you an IP address – it is expected that such IP address will be your IP footprint online and could be used for tracking you and enforcing access rights and content geo-targeting.
If you want to have freedom online, unblock websites, and access any content regardless of your physical location, then you will need to use either a proxy server or VPN software to spoof your real IP address and provide you alternative IP addresses.
For proxies, you can buy high-quality proxies from Smartproxy, MyPrivateProxy, and Shifter. Hola VPN, ExpressVPN, and SurfShark are some of the best VPN software out there.
Conclusion
From the above, you can see how IP addresses are assigned and unlike you will think – your IP address came a long way before it got into your hand. Interestingly, in most cases, you are using a dynamically assigned IP address that gets changed every now and then.
Because of the fact that IP addresses are unique and could be used to invade your privacy online, we advise our readers to make use of a proxy or VPN service to keep their real IP address hidden by spoofing it – this will also provide them freedom and help them unblock websites.






