What do you know about the similarities and differences between Remote Desktop, Proxy, VPN, VPS, and VLAN? In the article below, we will highlight the major differences and similarities and network them for you.

TL;DR: Here is a comparison table between Remote Desktop, Proxy, VPN, VPS, and VLAN:
| Feature | Remote Desktop | Proxy | VPN | VPS | VLAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Remote Access | IP Masking | IP Masking and Encryption | Virtual Dedicated Server | Virtual Local Area Network |
| Access to Programs and Files | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| Security | Relatively Secure | Limited Security | Secure | Secure | Secure |
| Encryption | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| Speed | Slow | Fast | Fast | Slow | Fast |
| Required Software Installation | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Cost | Free | Varies | Varies | Varies | Varies |
The networking space comes with a lot of remote access technology, each with its use case, strength, and weaknesses. While some of these tools can’t be compared because of their unique use cases compared to other technologies, newbies are fond of trying to compare them. There are about 5 of these technologies that are subject to such scrutiny because of their role in hiding IP addresses. These include Remote Desktop, proxy, VPN, VPS, and VLAN.
In this article, I will attempt to discuss the differences between these 5 technologies for you to understand how they differ. There are also a few similarities between these tools. Generally, you need to know that some of the tools are more similar in use cases than others, and as such, there is more to compare between them. For those that can’t be compared, we will only get to make a few mentions and descriptions since these tools are not as related as you will think at first glance.
Overview of the Network Tools
Before we can discuss the similarities and differences between these 5 tools, it is important we take a look at each of the tools individually.
-
Remote Desktop
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a network tool developed by Microsoft. This protocol is a secure network communication that enables remote access to a computer from another computer. It gives you remote management access, making it possible for you to control it, get access to the programs on the computer, and even access its files. With Remote Desktop, it will seem as if you are physically at the front of the computer. Access can be via the Internet or any other network, such as LAN and even Wi-Fi.
-
Proxy
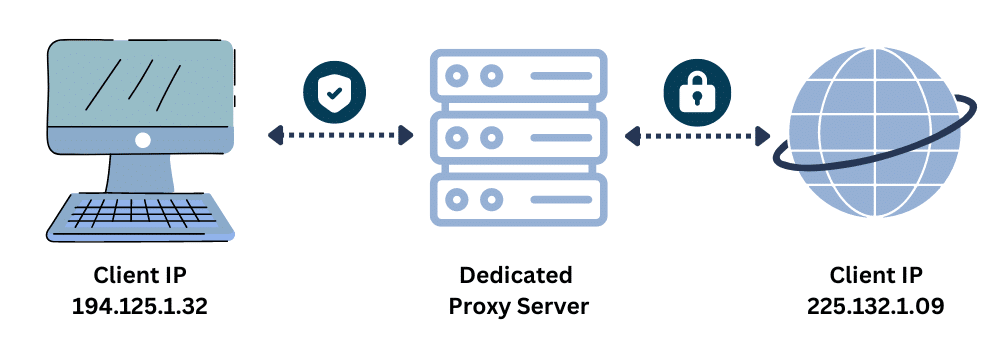
A proxy server is an IP masking tool that keeps your real IP address hidden from servers you interact with on the Internet. It is defined simply as an intermediary server that sits between your computer and web servers on the Internet. With proxies configured, requests from your computer do not go to their target servers straight.
Instead, they are routed via the proxy server, which then does the final routing. Because of this, the IP address seen is the IP of the proxy server, thereby keeping your own IP address hidden. Proxies do not require you to install any software — you only need the proxy address, port, username, and password.
-
VPN

A VPN is more like a proxy server — it is an IP masking tool. The major difference between proxies and VPNs is in the fact that VPN connections are routed via a secure and encrypted tunnel, making it difficult for any eavesdropper to actually know the content of the request packets.
Most VPN services will provide you with an app to install, which then forces all of your web requests via its server. This makes VPN software work at a system level and gives you the most privacy and security protection compared to proxies. However, it does have its own issues too.
-
VPS

A VPS is a Virtual Private Server (VPS) that uses virtualisation technology to mimic dedicated server environments within a shared server. It is basically a virtual machine that comes with an OS and even gives you superuser-level access. You can install any software that such VPS supports.
Take, for instance, with a Windows VPS; you are able to install windows apps on the server and use them even if you are using a Mac computer. While it seems to behave like a dedicated server, it still shares the underlying physical infrastructure with others on the same server, making it to be a little slow. It is sold usually as a hosting server.
-
VLAN
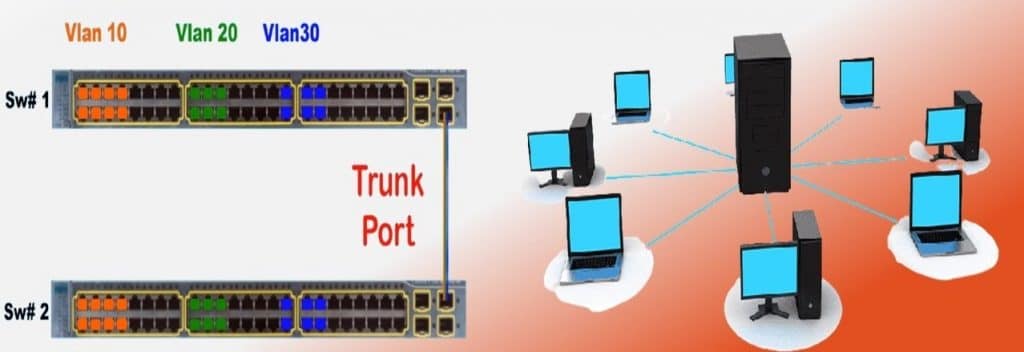
The only reason why VLAN is here is because of the virtual definition, as it is a lot different from the other tools described above. VLAN stands for Virtual Local Area Network.
A VLAN is the combination of one or more LAN networks into one logical network. This makes it possible for you to manage devices in multiple LANs as if they are in the same Local Area Network.
Let's say your organization uses different LANs for each floor of your office storey. With the help of VLAN, all of the LANs can be managed as one LAN using a VLAN.
Similarities Between Remote Desktop, Proxy, VPN, VPS, and VLAN

Before we move into discussing the difference between these tools, let's take a look at the similarities between them. All of these tools create a virtual connection, but the way the connection is created is one of the things that differentiates them. Take, for instance, Remote Desktop, which creates a connection between two computers, VPN, and proxy created between your device and web servers on the Internet, and VPS uses virtualization to make shared hosting look like dedicated hosting. For VLAN, virtualization is used to bring devices within different LANs under one manageable unit, like a single LAN.
Another similarity between most of these tools is the masking of IP addresses. Whether you make use of a Remote Desktop, VPN, proxy, or VPS, just know that you will be masking your IP address which gives you some form of anonymity as you access the Internet. However, it is important you know that most Internet users interested in hiding their IP address will either use proxies or VPN software.
Only a few users will decide to use a VPS or Remote Desktop just to mask their IP address. There are certain circumstances that Internet users will use VPS to benefit from the IP address it provides. For Remote Desktop, even though it changes your IP address, no one will use it for such a reason. VLAN is a little different from the others here as you just happen to take the ID of the single Internet route through which your device is connected to the Internet.
Differences Between Remote Desktop, Proxy, VPN, VPS, and VLAN
As stated earlier, the technologies powering these tools and their usage differ, so there isn’t much difference that is important for discussion. However, let's take a look at some of these.
1. Remote Access Level and Control

One of the major aspects these tools differ in is the remote devices they have access to and the level of access they have. Remote Desktop will provide you access to one device at a time. But the level of access you get is unrivaled by any of the tools.
With Remote Desktop, you can access all of the files on a remote computer, modify them, use the programs installed on them and even install new applications. In fact, remote access gives you access as someone physically sitting in front of the computer.
The next candidate at this level is VPS. For VPS, providers use virtualization to partition the server and make it look like you are using a dedicated server. Each partition will have its own Operating System (OS) and files.
Many of the VPS providers will provide you with superuser access to the VPS. While Remote Desktop gives you access to all of a remote computer, VPS gives you access to a partition of a server designed to look like a dedicated server.
In the case of a VLAN, it is no different from a regular LAN. There is a shared data resource center that devices on the network can have access to. Files not available on such shared data storage are not accessible, making it highly restrictive compared to VPS and Remote Desktops.
Both proxies and VPN software do not even give you access to any file whatsoever. What they basically do is accept your request and route it to your target server and then return the response to you when it is ready, which is usually instant.
2. Security Provision
How secure are all these 5 tools? It is important you know that each use a different type of security, and because they are fundamentally different, their vulnerability varies. For example, the Remote Desktop tool is protected by two security systems.
The first option is the standard security which uses RSA’s RC4 encryption algorithm to protect data transmission and ensure a secure connection. The other option provided is known as enhanced security. For this, security is outsourced to a third-party option such as Credential Security Support Provider (CredSSP) and Transport Layer Security Protocol (TLS).
In the case of a VPN, your web traffic is encrypted, making it difficult to eavesdrop. There are a good number of VPN security protocols, including IPSec, OpenVPN, SSTP, and WireGuard. As in the case of VPN, VPS provides end-to-end encryption using SSL technology.
On the other hand, a proxy is not the best technology in terms of security. This is because it does not provide you with any form of encryption. Data transported is available to eavesdroppers as plain text, which make them insecure. The VLAN technology is also not one of the most secure options. Read this article on Tofeno Security to discover why VLAN lags behind in terms of security.
3. Source of IP Address
As mentioned in the similarity section of this post, I stated that these tools all keep your IP address masked by replacing it with a different IP address. What is the source of this new IP address used, and how often can it be changed? Starting with Remote Desktop, the IP address used is the IP address of the computer you are accessing remotely. There is really not much flexibility as far as changing IP is concerned, except you are able to get the IP address of the remotely controlled computer to change.
For VPS, the IP address used will be the IP address of hosting, which can either be dedicated or shared. One thing you also need to know about VPS is that the IPs are datacenter IPs, and as such, some sites might block you if you try accessing them aggressively. The flexibility of changing IP is also not available.
Proxies and VPNs provide you the most flexibility in terms of VPN, with proxies being the absolute beast. Proxies get their IP address either from regular Internet users, as in the case of residential proxies, or via modems and sim cards, as in the case of mobile proxies. A good number of proxies get their IPs from the datacenter, as in the case of datacenter proxies.
The majority of VPNs also source their IPs from the datacenter. For VPN, you can change IP with just a button click. In the case of proxies, more methods are available, with even the possibility of automatic IP change after every request. For VLAN, this will depend largely on the router or source of the Internet used.
4. Platform and Installation
How do Remote Desktop, Proxy, VPN, VPS, and VLAN compare in terms of platform support, installation, and pricing? Starting with Remote Desktop, you can see it as the easiest among all of these tools. This is because the Remote Desktop tool comes installed in popular operating systems, including Windows and macOS. For this reason, all you only need to do is update the software. While the standard option is free, there are third-party Remote Desktop tools that come with some advanced features that you will need to pay to use.
In the case of proxies and VPNs, you will pay to use them. While there are free options available, you are better off running away from them because of their security and privacy risk. They are also worse in terms of performance. For proxies, you are not required to install any software in other to use them, as all you need is a proxy address, port, username, and password. In the case of VPN software, you will need to install an app. However, most of the top VPN vendors support popular Operating Systems and platforms.
In the case of VPS, there are options available to you in terms of Operating Systems. While an overwhelming majority of the providers offer Windows VPS, there are some that support macOS and other operating systems. VPS is a hosting service, and as such, you shouldn’t expect it to be free. The free options will be highly limited and not useful for any business usage.
5. Use Cases
Last on our list is the use case of each of the 5 tools. Needless to say, the tools have different use cases. For Remote Desktop, you can use it to access your computer remotely. This makes t easy for giving your device access to team members or even others outside of your organization.
In the case of a VPN, there is a whole lot you can use it for, such as hiding your IP address, blocking ads, evading trackers, and accessing geo-fenced content. Proxies are a lot more like VPNs, only that it does not block ads. Proxies are the most flexible in terms of changing IP, and that is why it is the go-to tool for web automation and Internet marketing in general.
VPS, on the other hand, is a hosting service. With a VPS, you can host websites, run web applications, and even store files on them. In the case of VLAN, it can be used for dividing large LAN setups into manageable units for easy management and administration.
Conclusion
Looking at the 5 items compared, you will see that each has its unique use case and, as such, shouldn’t even be compared with the other. Take, VPN can’t be used to host websites, and proxies won’t remotely control a different computer.
However, the comparison comes as a good number of people tend to expect some similarities because of the existence of virtualization in all of these tools.






